
Top 5 Best Online Colleges in Georgia – 2026 Comparison
Explore the best online colleges in Georgia for 2026. Compare top programs by cost, flexibility, accreditation, and career support to ...
Read More →
Top 5 Best Online Colleges in Georgia – 2026 Comparison Looking for the best online college in ...
Read more →.png)
You’ve probably heard the advice: “Keep your head down, work hard, and eventually, someone will ...
Read more →
If you’re searching for the best online college in Texas, you’re already making a smart move. Texas ...
Read more →
Explore the best online colleges in Georgia for 2026. Compare top programs by cost, flexibility, accreditation, and career support to ...
Read More →.png)
Potential won't get you promoted; results will. Drive your career growth by building undeniable promotion proof with credible skills. Learn ...
Read More →
Looking for an affordable, flexible online degree in Texas? Our 2026 guide ranks the top 5 online colleges by cost, ...
Read More →
University of the People or The Open University? Compare tuition, programs, accreditation, and student support to choose the right fit ...
Read More →
Learn why your resume might not be landing you interviews and discover actionable tips to enhance its effectiveness and relevance ...
Read More →.png)
Stop letting your hard work go unnoticed. Learn how to document your impact, make your value visible, and get the ...
Read More →
Too busy for career advancement? Our promotion plan for working professionals shows you how to get promoted in just 30-60 ...
Read More →
UoPeople vs UMPI YourPace 2026: Which affordable online university is right for you? We compare programs, flexibility, accreditation, and learning ...
Read More →
Trying to decide between University of the People and SNHU in 2026? Compare costs, programs, accreditation, financial aid, and flexibility ...
Read More →
Trying to decide between UoPeople and WGU? We break down costs, programs, flexibility, and support so you can pick the ...
Read More →
Compare Nexford University vs Rome Business School on cost, flexibility, accreditation, and career support to find the best online business ...
Read More →.png)
Thinking about an online MBA in Florida? Read this honest guide to see if it's the right fit or if ...
Read More →
Discover how to align your skills with the right job, rather than just chasing job titles, for a more fulfilling ...
Read More →
Stop waiting for permission to lead. Learn how to build a proof-first growth plan that makes your next career move ...
Read More →
Stuck in your career? Discover how an online degree helps Florida professionals secure promotions, build leadership skills, and achieve real ...
Read More →
Discover why African recruiters prefer concise, relevant resumes over lengthy, detailed documents and how this can improve your job application ...
Read More →
Understand the challenges African learners face in remote hiring and learn strategies to better navigate the global job market. ...
Read More →.png)
Comparing an online vs. traditional degree in Florida? This guide helps working adults analyze the true ROI based on cost, ...
Read More →.png)
Thinking of changing careers? Don't quit your job just yet. Learn how to 'date the role' and build a proof ...
Read More →
Looking for Quantic University alternatives? Compare the top 5 competitors in 2026 for affordability, flexibility, accreditation, and career outcomes. ...
Read More →.png)
Don't get played by vague promises and hidden fees. Learn to spot the red flags in higher education and avoid ...
Read More →
Discover five essential green flags to look for in a job to ensure a fulfilling and sustainable career. Learn how ...
Read More →
A guide for working adults in Florida. Learn strategies for time management, choosing the right program, and staying motivated while ...
Read More →
Tired of career situationships? Discover the top green flags in online degrees—flexibility, transparency, and support—and find a program that commits ...
Read More →
Explore open learning choices beyond traditional university! Discover the top 5 Open University alternatives in 2026. ...
Read More →
Explore open learning choices beyond traditional university! Discover the top 5 Open University alternatives in 2026. ...
Read More →.png)
Choosing an online degree in Florida? This guide for working adults covers what matters: accreditation, outcomes, real flexibility, and ROI. ...
Read More →
Explore UMPI alternatives in 2026! Discover the top 5 college competitors, offering flexible online courses & master's programs. Read today. ...
Read More →
What is intrapreneurship, and why is it important in business? Learn how fostering innovation within your organization can drive growth ...
Read More →
This article explores the highest-paying jobs in Idaho. Read on to dig deeper into their job descriptions, expected salaries, and ...
Read More →
In this article, we will discuss the top 10 highest paying IT jobs and careers in 2026, including their salaries. ...
Read More →
Entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship are two buzzwords that have been used interchangeably, but in reality, they have very distinct differences. An ...
Read More →
As they say in the classics, in business there are leaders and then there are followers. And you'd rather be ...
Read More →
In a rapidly evolving job market, pursuing a master's degree is a strategic move to enhance your earning potential and ...
Read More →
Over the last decade, technology development and innovation have been at an all-time high. And what powers all this is ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying jobs in Oklahoma for 2026, including salaries and job opportunities in Oklahoma City. Find ...
Read More →
In this article, you can find a rundown of all the highest-paying jobs in South Carolina. Each job title is ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest-paying legal jobs for 2026, including salaries, to help you choose the right path in the ...
Read More →
Explore the top 10 highest paying master's degrees in 2026, with the potential to earn salaries over $100K. Discover your ...
Read More →
Being a leader in any organization is no easy task. Not only are leaders responsible for their actions, and the ...
Read More →
Discover the highest paying online and remote jobs in 2026, from data science to mobile development, this article discusses it ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying jobs in Colorado, including CEO, Physician, and more. Find the best paying jobs available ...
Read More →
An online MBA degree can be your gateway to unlocking better career opportunities. With an online MBA, you’ll learn more ...
Read More →
This article talks about vital information about the highest-paying jobs available in New Hampshire, including the full job description, estimated ...
Read More →
Discover how a Master of Science in Entrepreneurship program equips you with the skills and connections to launch your startup ...
Read More →
While consumer applications of the Internet of Things offer comfort and convenience, the impact of IoT on business is far more significant. This ...
Read More →
As many industries evolve and technology advances, new high-paying roles may emerge, and the landscape of high-paying positions within basic ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying jobs in Hawaii, including CEO, Physician, and more. Find the best paying jobs available ...
Read More →
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, possessing an entrepreneurial mindset is becoming increasingly crucial. Whether you're a student, a small ...
Read More →
Ever heard the terms 'revolving doors' or ' a toxic workplace culture?' Creating a perfect company and corporate culture can ...
Read More →
Explore the potential salary outcomes after earning your Master's in Entrepreneurship. Compare earnings based on experience and education. ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest-paying finance jobs for 2026, including salaries and job responsibilities in the finance industry. Find your ...
Read More →
If all companies’ business models stayed the same, they would fail. In recognition of the need to evolve and increase ...
Read More →
There is no denying that accountants are very important. They keep businesses afloat by keeping accurate records, monitoring finances, and ...
Read More →
Discover the highest paying medical and healthcare jobs in 2026, from a pharmacist to a medical doctor, this article discusses ...
Read More →
Some ways to pay for your MBA tuition include student loans, fellowships, scholarships, student loans, employer sponsorships, and assistantships. ...
Read More →
Energy jobs pay well and as such, people in the energy sector with the right skills sets can now build ...
Read More →
As a Kenyan working professional, pursuing an online MBA program can open up new opportunities for you without requiring you ...
Read More →
They say that specializing in a particular field or area of study can offer several advantages when pursuing a degree ...
Read More →
In this article, let us explore the highest-paying marketing and advertising jobs. Continue reading to get a sneak peek at ...
Read More →
This article covers the highest-paying jobs in Ohio, including job descriptions, requirements, and salary information. ...
Read More →
Explore the Highest-Paying Jobs & Careers, from AI to Surgeons. Learn the skills, education, and salaries needed for success in ...
Read More →
Thanks for your interest in writing a guest post for Nexford’s blog, NXU Insights. Here’s everything you need to know ...
Read More →
Explore the best-paying engineering jobs. From Aeronautical to Nuclear Engineering, explore lucrative paths shaping innovation and technology. ...
Read More →
Nowadays, side hustles are a great way for people in Nigeria to earn a little extra cash outside of their ...
Read More →
If you are an economics major in Nigeria, you may be wondering what kind of career options are available to ...
Read More →
In the digital age, and new digital economy, digital marketing is one of the highest searched for terms on search ...
Read More →
Venture capital (VC) is a type of private equity investment that provides funding to early-stage companies or startups with high ...
Read More →
This article looks into the high paying jobs available in Nebraska, including their full job description, essential qualifications, average salaries, ...
Read More →
Having a psychology degree can open a window on the world of human behavior and neural cognizance and also ensure ...
Read More →
This article discusses all the important job details you need to know about the high-paying jobs available in Vermont in ...
Read More →
Discover the advantages of getting an MBA or MS as an entrepreneur. Learn if you really need a business degree ...
Read More →
Time. It's an extremely valuable commodity and sadly one that it would seem abundant on one hand, but very scarce ...
Read More →
This article features the 10 highest-paying jobs available in Rhode Island in 2026. In addition to job titles, the article ...
Read More →
The field of technology offers a wide range of lucrative career opportunities. With the rapid advancements in tech, the demand ...
Read More →
In this article, we will explore the top 15 highest paying jobs in Washington D.C, shedding light on the requirements, ...
Read More →
Entrepreneurship is a dynamic and exciting field that drives economic growth, fosters innovation, and empowers individuals to transform their ideas ...
Read More →
Entrepreneurship is the act of creating or starting a new business venture. It is the process of identifying a need ...
Read More →
There are many factors that affect your chances of getting a high-paying career. This includes small-scope ones like educational attainment ...
Read More →
Discover how long it takes to earn a degree in entrepreneurship online and learn about the career opportunities that come ...
Read More →
The tech industry is one of the fastest-growing fields in the world today. The Internet has dominated almost all aspects ...
Read More →
If you are looking for a high paying career, New Jersey offers some of the highest-paying jobs with often a ...
Read More →
Entrepreneurship is one of the biggest driving forces in today’s economy. All across the world, but particularly in countries like ...
Read More →
A BBA is one of the most popular professional degrees that will teach you about the fundamentals of management and business and help ...
Read More →
There is a marketing term that goes, "teamwork is dream work." Sounds easy enough, but true teamwork can only come ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying retail jobs for 2026, including salaries and hourly wages. See which retail positions offer ...
Read More →
Pursuing an MBA program can open up a whole new world of possibilities for you. With an MBA degree, you ...
Read More →
To grow your existing business, or grow your small business or startup in the global market space can be a ...
Read More →
The demand for software engineers is on the rise, with the number of jobs available in the field expected to ...
Read More →
Wondering what fulfilling jobs await you in the dreamy state of Maine? Explore the top 10 highest-paying jobs in Maine ...
Read More →
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) is the ultimate form of remote working, and its popularity is soaring in the Philippines ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying jobs in Arizona, including Dentist, Pilot, and more. Find the best paying jobs available ...
Read More →
In this article, we'll explore the highest-paying sales jobs in 2026, along with everything you need to know about them-- ...
Read More →
Earning an MBA degree from the right institution can widen your options outside of the job market. However, in an ...
Read More →
This article explores the highest paying jobs available in Mississippi —from nurse practitioners to physicians, corporation jobs, and many more. ...
Read More →
Find the top 10 highest paying jobs in education for 2026, including salaries, to plan your high-paying career in education. ...
Read More →
Here’s a detailed list of the highest paying jobs available in South Dakota. It includes all the vital job details, ...
Read More →
Online learning has totally changed the way students can earn undergraduate and postgraduate degrees without having to leave their homes. ...
Read More →
Find the top 10 highest paying jobs in nursing for 2026, including salaries, to plan your high-paying career in nursing. ...
Read More →
A common trait among many executive leaders and business managers is a continuous pursuit of knowledge and education. ...
Read More →
If you're a biology graduate in Nigeria, you might be wondering what the highest paying jobs are that you can ...
Read More →
An MBA means salary boosts, networking opportunities, enhanced skills, and higher acceptance rates. That sounds great, but you might still ...
Read More →
Explore the top 15 highest paying entry-level jobs for 2026, including salaries and job duties. From data scientist to sales ...
Read More →
Check out this article to get vital information about the highest-paying jobs in Missouri. From job descriptions to salary information, ...
Read More →
Discover the best master degree options for business owners looking to succeed in the business world. Boost your career with ...
Read More →
Mass communication is a diverse and dynamic field that offers a wide range of rewarding career opportunities. Professionals in this ...
Read More →
In the fast-paced world of entrepreneurship, risk taking is a crucial factor that can make or break a business. Successful ...
Read More →
The best way to progress your career has been proven to be by earning an MBA from a reputable organization ...
Read More →
Chemistry is a fascinating field that deals with the study of matter and its properties, reactions, and transformations. In Nigeria, there ...
Read More →
The great debate rages on as to whether it is better to be a generalist or specialist. So which way ...
Read More →
Discover why studying entrepreneurship is crucial for aspiring entrepreneurs. Explore the importance of entrepreneurship education for building essential skills and ...
Read More →
Considering a career in entrepreneurship? Discover the pros and cons of becoming an entrepreneur and decide if it's the right ...
Read More →
Being in customer service can easily be referred to as a 'Marmite' job. You either love it or you hate ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying jobs in Virginia, including medical doctor, dentist, and many more. Get to know the ...
Read More →
Comparing the similarities and differences between a Masters in Entrepreneurship and an MBA degree can help you determine the best ...
Read More →
In this article, we’ll dig deeper into the important job details of the highest-paying jobs available in Connecticut in 2026, ...
Read More →
Is an MBA worth it for engineers? You’ve probably asked yourself this question if you’re at the point in your ...
Read More →
If you want to build and grow a business, you have to start somewhere. If you’re considering a career path ...
Read More →
Supply Chain management is so broad based and extensive that anyone choosing this career path can find something to fulfill their goals ...
Read More →
Geology is a fascinating and rewarding field of study that deals with the Earth's structure, composition, and history. It is ...
Read More →
Explore top high-income skills for 2026: Data Analysis, Software Development, UX, Web Development, Project Management, and more. Boost your career ...
Read More →
With forms of energy and the types of power generation fluxing and changing year by year, such as solar energy ...
Read More →
No one wants to remain in the same spot, but how do you advance your career opportunities while managing a ...
Read More →
Is a degree in entrepreneurship worth it? Learn about the skills, advantages, and potential careers with an entrepreneurship degree. ...
Read More →
In today's competitive business landscape, networking has emerged as a crucial tool for success. Whether you are a business owner ...
Read More →
English. They say that it is the most spoken language on the globe, with more than 1.45 billion waxing lyrical in ...
Read More →
Customer service or consumer services. It's one of those Marmite jobs. You either love it or you hate it. Being ...
Read More →
In a continent with 1.26 billion people, so many countries, and so many economies, it makes sense that job opportunities ...
Read More →
Being a CFO has transformed over recent years. Today it’s more challenging, strategic and embraces cutting-edge technologies. Let's discuss the ...
Read More →
Thanks to an ever-widening gap between skilled and unskilled workers in Egypt, many employers are struggling to hire top talent ...
Read More →
They say that true leaders are born and not created. Forbes maintains that leadership can be taught and learned, but ...
Read More →
An ecommerce degree can set you on the path toward a successful digital marketing career or a thriving ecommerce business. ...
Read More →
Discover the highest paying geology jobs in 2026, from hydrogeology to geoscience, this article discusses it all. Read more! ...
Read More →
Worried about writing as part of your studies? We get it. Meet Kerry Conlan, Nexford’s Writing Coach, who’s here to ...
Read More →
In this article, we’ll explore the highest-paying jobs in Massachusetts, paying close attention to details like job description, career outlook, ...
Read More →
Are you wondering if an Artificial Intelligence degree is worth it? In this article, we'll explore the advantages, disadvantages, and ...
Read More →
Discover the highest paying tech jobs and careers in 2026, from full-stack developers to software architects, this article discusses it ...
Read More →
An MBA (or Master’s of Business Administration) degree can be a great way to advance your career and unlock new ...
Read More →
Skills vs Competencies. How do they differ from each other? Get the Nexford rundown below! ...
Read More →
When it comes to starting a career, it's important to consider the financial rewards of the job in addition to ...
Read More →
Technology is changing the world, affecting the way we store and prepare our food, right down to how we do our work ...
Read More →
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the most important details of the highest-paying jobs in Pennsylvania, including ...
Read More →
With the globalization era gaining steam now more than ever, businesses and employment are no longer confined to a local ...
Read More →
This article talks about the highest-paying jobs in Tennessee in detail. We’ve included information about their job description, employment outlook, ...
Read More →
In order to make a career out of communication, a communications degree will have you focus on honing communication skills, ...
Read More →
Discover the best degrees for aspiring entrepreneurs to become an entrepreneur and how a degree can help you become a ...
Read More →
Entrepreneurship is a mindset and a way of life that involves the creation and management of a successful business venture. ...
Read More →
In every realm of life, from the corporate world to community organizations, effective leadership is the bedrock upon which triumphs ...
Read More →
A degree in business opens up the doors to job stability and security, career and time flexibility, and, most of ...
Read More →
In this article, we'll explore the essential details about the top jobs in Nevada with high pay. Aside from the ...
Read More →
In 2026, the business world continues to reward leadership and expertise with substantial paychecks. From executives to financial managers, explore ...
Read More →
Global connectivity and the shift to remote work have created new and exciting careers. Nowadays, people can work for companies ...
Read More →
Entrepreneurship is a popular and exciting topic, especially for those who dream of starting their own business or have already ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying healthcare administration jobs in 2026, including salaries and job duties. Find your next healthcare ...
Read More →
Diversity is a word that is on everyone's lips right now. Equal representation and inclusivity in sport, business, the media, ...
Read More →
40 years ago, if you dedicated yourself to a company, you would have a career for life. How times have ...
Read More →
As an ambassador for young Nigerians getting a world-class education, Dr. Oby Ezekwesili is a staunch believer that with equal ...
Read More →
Effective communication is vital in all forms of life and of course even more vitally across all businesses and industries. ...
Read More →
Choosing the right course of study is a crucial decision that can greatly impact your career and earning potential. In Nigeria, ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest-paying biotech jobs in 2026. From biomedical engineers to CMOs, explore lucrative careers in cutting-edge science. ...
Read More →
Discover the highest paying chemistry jobs and careers in 2026, from chemical technicians to forensic scientists, this article discusses it ...
Read More →
Engineering is one of the most technical endeavors known to man. It is the practical application of different disciplines as ...
Read More →
In this guide, we’ve put together everything you need to know about the highest-paying jobs for women. From job description, ...
Read More →
In today's interconnected world, international relations play a crucial role in shaping diplomatic, economic, and social interactions between nations. Nigeria, ...
Read More →
In this article, let's explore the highest-paying jobs in the USA, including their earning potential, job description, and outlook. ...
Read More →
This article explores the 10 highest-paying Jobs in Kentucky in 2026, taking a closer look at all the important job ...
Read More →
In this article, we'll explore all the vital information about the highest-paying social work jobs, including their job descriptions, salary ...
Read More →
The field of computer science offers a wide range of lucrative career opportunities. With the rapid advancements in technology, the ...
Read More →
If entrepreneurs all did business in the same way, in the same industries, in the same marketplace, and with the ...
Read More →
Discover the highest-paying jobs in the world in 2026. This article discusses all, from data science to investment banking. Read ...
Read More →
In this article, we'll explore the highest-paying real estate jobs in 2026, along with everything you need to know about ...
Read More →
Entrepreneurship is the process of creating and running a new business venture in order to generate profits. It is a ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying job opportunities in North Carolina for 2026, including Nurse Practitioner and Chief Information Officer ...
Read More →
Business process outsourcing (BPO) is the delegation of one or more IT-intensive business processes to an external provider that, in ...
Read More →
Discover the highest paying federal government jobs in 2026, from a finance manager to general attorney, this article discusses it ...
Read More →
After several challenging years, the world is finally beginning to bounce back. Economies worldwide—including South Africa’s—are steadily returning to their ...
Read More →
Discover the highest-paying public health jobs in 2026, how much the positions pay, and the requirements to be qualified for ...
Read More →
Choosing a career can be daunting, especially for people fresh from university. Job opportunities in Nigeria are increasing, and there ...
Read More →
You would have been living under a rock if you did not know how artificial intelligence is set to affect ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying mechanical engineering jobs in 2026, including average salaries and job duties. Find the best ...
Read More →
Cybersecurity is touted as having a zero unemployment rate. It is one of the fastest-growing and in-demand professions in the ...
Read More →
Explore the Top 10 Highest Paying Marine Biology Jobs in 2026, including salaries. Dive into careers from Research Assistants to ...
Read More →
The recent global pandemic has highlighted the need for a robust healthcare sector. Their skills and service proved vital in ...
Read More →
Obtaining a degree in business administration opens up a wide range of lucrative career opportunities. With the ever-increasing demand for ...
Read More →
In today’s global economy, having the right skill set is crucial. Decades ago, it was enough to have a few ...
Read More →
If you're a job seeker in Nigeria, you're probably interested in knowing which companies offer the highest salaries. Salaries in ...
Read More →
With the global shift to remote work, outsourcing companies are taking the lead in the Philippines. The country offers a ...
Read More →
Biochemistry is the branch of science that deals with the chemical processes that occur within living organisms. It is a ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying jobs in Arizona, including Dentist, Pilot, and more. Find the best paying jobs available ...
Read More →
In this article, we're taking a deep dive into the social science jobs that offer the highest pay, job descriptions, ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying jobs in Texas for 2026, including salaries up to mid six figures. Live comfortably ...
Read More →
Entrepreneurship refers to the process of starting and managing a business venture in order to create value and achieve financial ...
Read More →
In this article, we'll explore everything you need to know about the highest paying HR jobs, including their description, the ...
Read More →
Discover the highest paying biochemistry jobs in 2026, from biomedical to food science, this article discusses it all. Read more! ...
Read More →
With the increasing adoption of digital technologies, online jobs are becoming popular in Nigeria. They offer the flexibility to work ...
Read More →
Five years ago, artificial intelligence was just a futuristic term that people feared as naysayers were predicting large scale job ...
Read More →
Discover the top 15 highest paying jobs for economics majors in 2026, including salaries and potential career paths for economics ...
Read More →
Discover the top 15 highest paying international relations jobs for 2026, including salaries and job opportunities. Find the best international ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying jobs in New York City for 2026, including salary information and job duties. Find ...
Read More →
Discover the highest-paying jobs with a biology degree in 2026. This article discusses all, from medical doctors to microbiologists. Read ...
Read More →
Are you looking to build a successful career in the federal government in Nigeria? If so, you might look into ...
Read More →
In recent years, Kenya has seen some of the biggest economic booms in the continent. The rise of the internet ...
Read More →
Discover the top 15 highest paying accounting jobs for 2026, including salaries and job opportunities. Find the best accounting career ...
Read More →
Discover the top 10 highest paying science jobs for 2026, including salaries and career opportunities in research and the best ...
Read More →
With the world’s economies recovering and beginning to grow, there is a great opportunity to start or change your career. ...
Read More →
Learn how to make your work visible and promotable by translating tasks into outcomes, building consistent visibility habits, and starting ...
Read More →
Tired of an education system that goes nowhere? Learn how Nexford offers affordable education and real skill-building for your career ...
Read More →
Stop fearing the robot takeover. Learn the practical skills managers need to lead in the age of AI, from strategy ...
Read More →
Need flexibility and value? Compare 2026 WGU alternatives offering self-paced learning, global pricing, and career coaching for working adults. ...
Read More →-3.png)
You don't need to know Python to lead AI initiatives. Learn how to bridge the gap between tech and business ...
Read More →
Nexford vs WGU made simple. Compare tuition, pacing, and support to find the online degree path that feels right for ...
Read More →
Meet the new MSAI at Nexford University. No coding required—just the strategy, leadership, and practical skills you need to lead ...
Read More →
Top 5 SNHU alternatives for 2026: compare affordable, flexible online programs (Nexford, WGU, UoPeople, UF Online, FHSU) to find the ...
Read More →
Learn how to effectively audit your career skills and progress in January with a structured approach to ensure consistent growth ...
Read More →
Choosing between Nexford and SNHU? Explore the key differences in price, flexibility, and support so you can pick the online ...
Read More →
Learn how to advance your career within your current organization by expanding influence, building relationships, enhancing visibility, demonstrating leadership, and ...
Read More →
Discover how to earn a German degree. See the recap of our Nexford to Constructor University pathway webinar, including scholarships, ...
Read More →Deciding between Nexford vs WGU Texas? We compare affordability, flexibility, and curriculum to help Texas adult learners choose the right ...
Read More →
Explore why Texas is a top destination for online education. Discover flexible and affordable online bachelor's and master's degree programs ...
Read More →
Stop resetting your career every January. Instead, build on your existing skills and refine your career for sustained growth. Discover ...
Read More →
Compare Nexford vs WGU Texas for career advancement. Discover which online university offers the best ROI, modern curriculum, and flexibility ...
Read More →
Missed our Future of Finance webinar? Read the recap to learn how AI, CFI certifications, and project-based learning are redefining ...
Read More →
Compare Nexford vs SNHU for Texans. This guide breaks down affordability, flexibility, and curriculum to help you choose the best ...
Read More →
Explore how different generations approach the job search and what they can learn from each other to stay relevant, confident, ...
Read More →
Mentorship isn't a formal marriage—it's about smart questions and real feedback. Here are 5 actionable takeaways from our session with ...
Read More →
Forget the career ladder. Elena Shchichkina reveals the rebellious, results-driven playbook behind her rise to CPO of a global animation ...
Read More →
Is your career AI-proof? Discover the top 5 actionable insights from our expert panel on how to stay relevant, boost ...
Read More →
The easy mode is over. See why investor Iyinoluwa Aboyeji says founders must be profitable on seed capital & use ...
Read More →
Unlock the secrets to driving impactful AI transformations and leading with confidence in the digital age. ...
Read More →
Explore how different generations are reshaping the workplace, leveraging AI, and redefining career success in a rapidly evolving job market. ...
Read More →
Emotional intelligence is important as it lets you understand and manage emotions linked to academic achievement, decision-making abilities, and lifelong ...
Read More →
Discover how long it takes to earn a masters degree in entrepreneurship, including MBA, MS options and opportunities for graduate ...
Read More →
Learn how to navigate career transitions in the AI era with adaptable strategies, skill-building tips, and mindset shifts to future-proof ...
Read More →
Kenyan University Strikes: Online Education and Affordable Degrees with Nexford University an affordable online university. ...
Read More →
Nexford University vs. University of the People: 2026 university comparison. Explore affordability, accreditation, enrollment, tuition and value for money. ...
Read More →
Exploring University of the People alternatives? Compare 2026’s top online universities that deliver global affordability, flexibility, and accredited degrees. ...
Read More →
Accelerate your career with a 9-month MBA program! Earn your MBA in just 9 months and graduate faster. A smart ...
Read More →
Discover the affordable cost of an online BBA degree at Nexford University. Learn about transparent tuition, flexible pay-per-course pricing, and ...
Read More →
Explore the promising future of the Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) degree in 2025. Discover its career benefits, scope, salary ...
Read More →
Nigeria’s skills gap widens as graduates lack job-ready skills. Explore key lessons and solutions for the nation’s future growth. ...
Read More →
Earn your Bachelor's in Business Administration in 12-18 months with accelerated degree programs. Compare fast-track options for working professionals and ...
Read More →
“Frankly, most other applicants don’t have an MBA from Dartmouth and $200,000 in loans to repay.” That’s what a candidate ...
Read More →
Discover the real return on education. See how Nexford alumni achieve rapid career progression, global jobs, and positive ROI with ...
Read More →![Is Nexford University Accredited [2026 Status]](https://www.nexford.edu/hubfs/Nexford-3.png)
Is Nexford University Accredited? Find out about this university's accreditation status, including Distance Education Accrediting Commission info. ...
Read More →Learn how AI skills are becoming essential for hiring and higher education, changing what employers and students expect from universities. ...
Read More →AI is reshaping careers. Discover how workers and employers are adapting through reskilling, reinvention, and AI fluency. ...
Read More →
Optimize your LinkedIn profile using AI tools to attract recruiters by enhancing your photo, headline, About section, and experience with ...
Read More →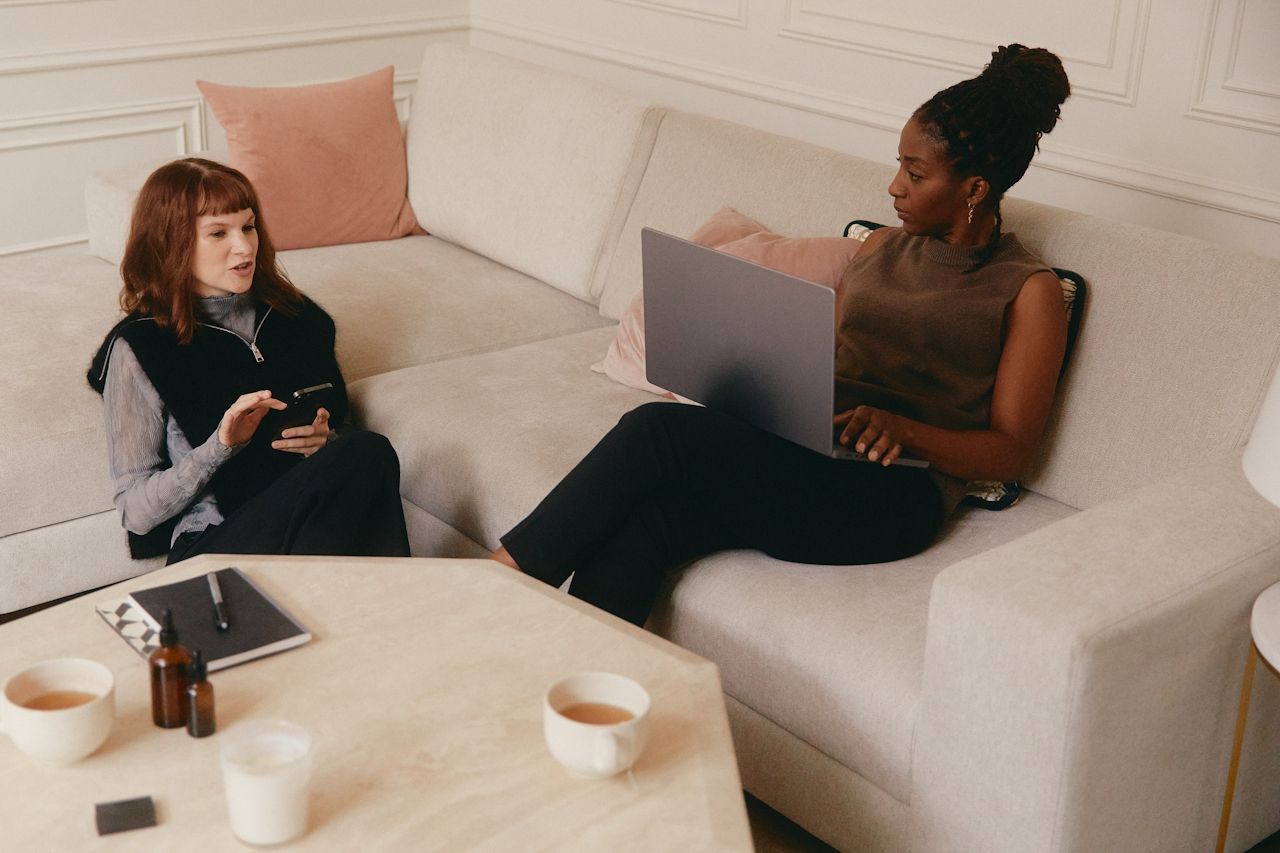
Nexford University Reviews: 2026 Student Insights. Uncover what learners say in this university review. Get honest insights and explore the ...
Read More →
Explore the top 10 highest paying pharmacy jobs in 2026, including salaries and job descriptions. Discover lucrative career opportunities in ...
Read More →
Make your career switch count. Get the flexible online degree designed for real-world impact—and move up fast with skills employers ...
Read More →
Struggling to grow at work? Learn how to move up with actionable career growth tips, online degrees, and steps to ...
Read More →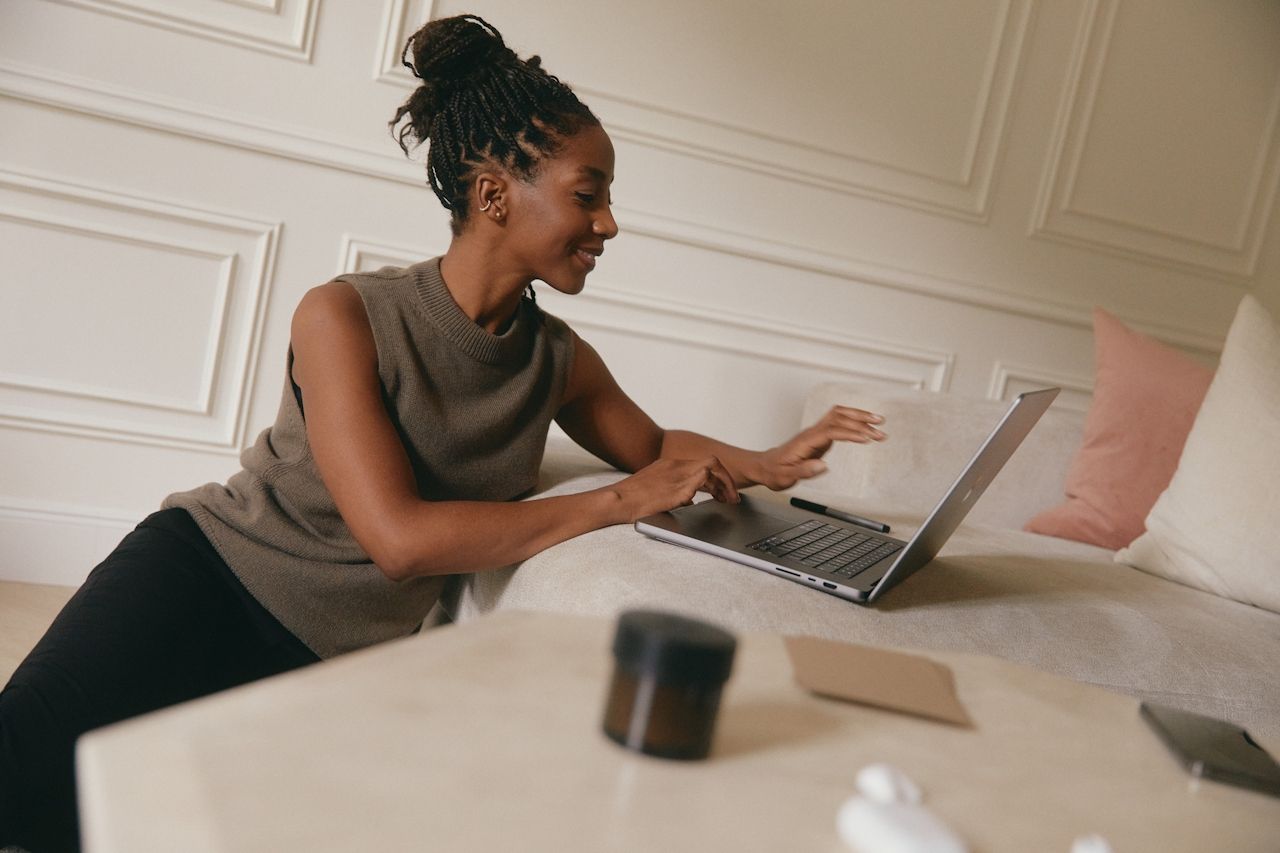
Discover why soft skills and personal branding are crucial for future-ready careers in an AI-driven world. Learn how to leverage ...
Read More →.jpg)
For millions of people around the world, their skills got them to where they are today. But in a world ...
Read More →
It’s no secret that higher education has become one of the most inefficient industries in the world. The cost of ...
Read More →
Strategies for professionals over 50 to stay competitive: keep learning, refresh your brand, show adaptability, maintain a youthful approach, and ...
Read More →
Nexford University updates its philosophy to integrate AI use in its courses, preparing students for future workplaces, emphasizing AI mastery, ...
Read More →
Explore the latest university ranking for 2026. Discover where we stand, plus info on tuition and more about Nexford University. ...
Read More →
Learn how to make your resume stand out using AI tools for concise, impactful, and customized applications that impress recruiters. ...
Read More →
Traditional universities drifted away. Nexford stays career-first, flexible, and debt-free—built for the real world. ...
Read More →
Nexford University vs. Quantic in 2026: A detailed comparison. Explore which online MBA program best fits your career goals. Find ...
Read More →
Don’t settle for a degree that looks good on paper but goes nowhere. Learn how to choose one that builds ...
Read More →.png)
Keep getting passed over for promotions? Learn how to build skills, boost visibility, and position yourself for career growth this ...
Read More →.png)
Switch careers without starting over. Discover the best degrees for career changers in 2025 and fast-track your next move. ...
Read More →-1.png)
Discover why 83% of online programs cost more than in-person classes and how our transparent, affordable approach offers a better ...
Read More →
Businesses and organizations recognize project management as being crucial to their performance and success ...
Read More →
The increased demand for product managers has meant that many people are considering it as a career. To be successful, ...
Read More →
Today’s world is becoming more and more connected as the push for globalization intensifies. Businesses see expanding operations to multiple ...
Read More →
Recent BBA graduate Progress Udoh really means business and is building an import/export company that he hopes will take the ...
Read More →
How you influence other people can be the difference between success and failure in life, but more importantly, in the ...
Read More →
Artificial intelligence is adding a new dimension to how we do business. With it, companies can create intelligent workflows that automate ...
Read More →
With many workers struggling to cope with the latest digital technologies and skills gaps appearing, it’s now a case of ...
Read More →
Many companies today offer some form of tuition help as part of your professional development — especially if you can ...
Read More →
The advancement of technology has meant a massive amount of data is processed every single day. It’s shaping our future ...
Read More →
Community College vs. Nexford University: Which is right for you? Compare affordability, flexibility, and career-focused learning to find the best ...
Read More →
Thinking of going back to school? Learn how to switch careers, stay employed, and avoid burnout with flexible, future-proof education ...
Read More →
Discover 4 flexible, affordable paths to earning a degree in under 2 years. Perfect for busy adults looking to advance ...
Read More →
Achieving your dream of studying for your degree and realizing a successful career starts with JAMB. Or does it? ...
Read More →
Advance your career without burning out. Earn a flexible, affordable degree on your schedule—without sacrificing work or life. ...
Read More →
Get ahead—no debt, no nonsense. Level up with job-ready skills that unlock real career growth without unnecessary expenses. ...
Read More →-1.png)
Kickstart your career—discover flexible, affordable ways working adults can earn a degree and move up, all on your schedule. ...
Read More →
Career advice aimed at recent and soon-to-be graduates: 5 smart moves for career networking, LinkedIn & more. Start your career ...
Read More →
AI is changing the rules. Learn the skills to stay ahead, stand out, and turn career goals into real-world wins ...
Read More →
Discover the best paying university degrees for high salary jobs in UAE. Find college degrees leading to the highest-paying graduate ...
Read More →
Discover the essential mindset shift from founder to CEO that drives growth in 2025. Learn how to build effective organizational ...
Read More →
Uncover the new approach to achieving product-market fit in 2025, as outdated strategies no longer suffice. This essential three-step guide ...
Read More →
Navigate the challenges of raising capital in 2025 with this essential guide for founders. Discover the differences between bootstrapping and ...
Read More →
Explore the future of marketing through five essential jobs that blend creativity, technology, and data-driven strategies. Learn how roles like ...
Read More →
Learn about the risks of not upskilling in today's fast-evolving job market and how skill-based education can future-proof your career ...
Read More →
Discover the top AI careers of 2025 and the essential skills you need to succeed in this rapidly evolving field. ...
Read More →
Join us for an insightful episode of the NexPulse Speaker Series as we welcome Gerald Beuchelt, Chief Information Security Officer ...
Read More →
Join us for an insightful episode of the NexPulse Speaker Series, featuring Marc LeVine, Talent Acquisitions Leader at Thermo Systems. ...
Read More →
Join us for an insightful episode of the NexPulse Speaker Series as we sit down with Nuno Fernandes, President of ...
Read More →
Discover how AI is transforming dealmaking, legal practice, and the future of work in this episode of the NexPulse Speaker ...
Read More →
Unlock the secrets to entrepreneurial success with Nicole Chamblin, Founder of Visions Productivity Solutions, in this episode of the NexPulse ...
Read More →
Discover the inspiring journey of Rod Danan, Founder and CEO of Prentus, in this exclusive episode of the NexPulse Speaker ...
Read More →
Higher education is often seen as a ticket to a successful career — but it comes at a cost. For ...
Read More →
The job market today stands still for no one. It’s highly competitive, so much so that it’s not enough to ...
Read More →
Your education is one of the most important investments you’ll ever make. But that doesn’t mean it has to be ...
Read More →
AI skills are no longer a “nice-to-have” for tech professionals — they’re a necessity for anyone looking to thrive in ...
Read More →
Are you looking for the next steps to advance your career without wasting time and money? A business graduate degree ...
Read More →
Can you really level up your career while working full-time? Short answer: Absolutely. ...
Read More →
We all know college loans are expensive. The average student debt is $35,530 from a public 4-year college and a ...
Read More →
A bachelor’s degree has always been seen as a gateway to expanded opportunities and earning potential. But in today’s increasingly ...
Read More →
Nexford understands why you’re making time to build better skills. We design courses with your end goals (and busy schedule) ...
Read More →
Go to college, get a good job. That’s the simple two-step process that many people plan and bank on. But ...
Read More →
College has long been seen as the default path to success — a four-year ticket to a better job, a ...
Read More →
How do you take an idea (a great idea!) and turn it into a viable business? The statistics can be ...
Read More →
Your education is a big decision. You deserve to know exactly what you’re signing up for. That’s why we created ...
Read More →
Change isn’t just coming — it has already arrived. Companies that embrace digital transformation are thriving, while those that don’t ...
Read More →
Let’s get one thing straight: Paying less for college shouldn’t mean sacrificing quality. Unfortunately, lots of people think the opposite. ...
Read More →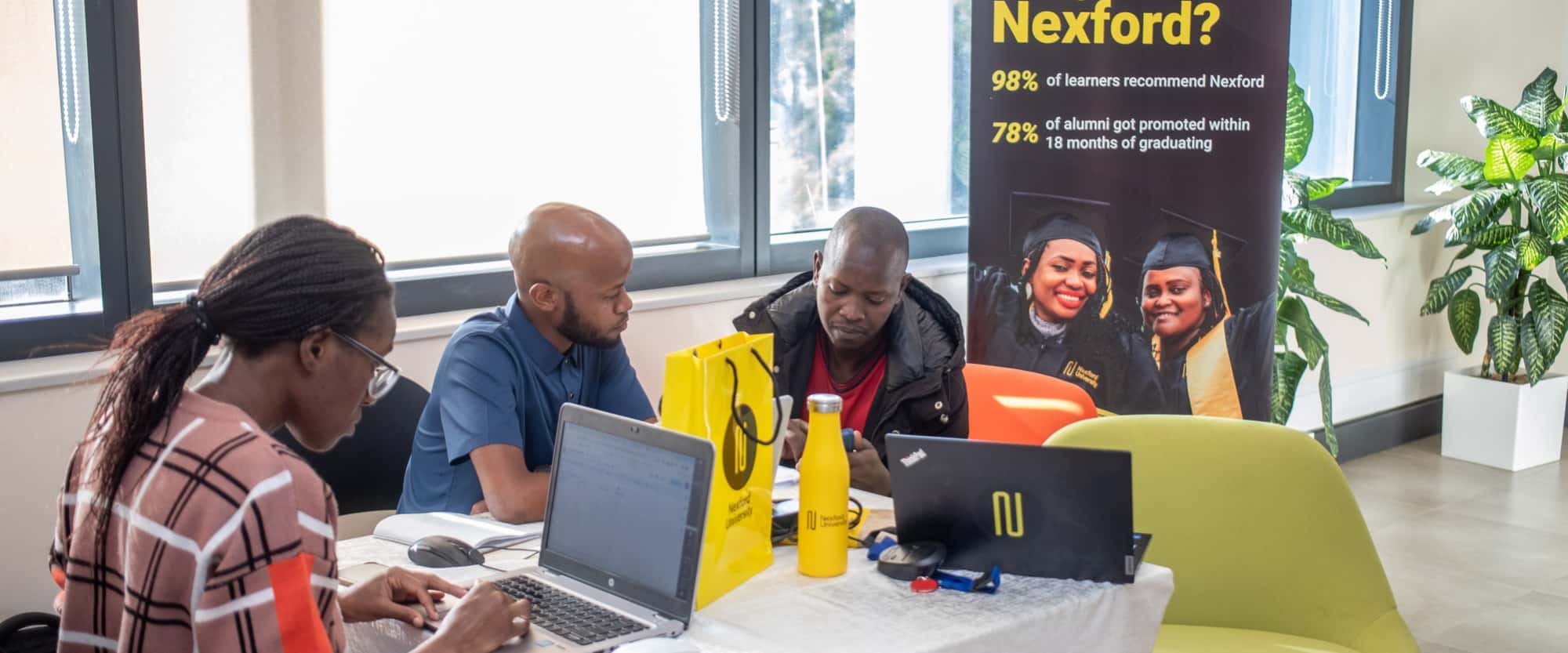
In a bold step toward building a more skilled and future-ready workforce, Kenya Airways (KQ) has joined Nexford University’s SkillBridge ...
Read More →
The professional landscape is evolving faster than ever. With technological advancements and industry shifts, staying competitive means adapting and developing ...
Read More →
This year, March 8, 2025, marks another inspiring International Women’s Day, and this year’s theme, #AccelerateAction, reminds us to advance ...
Read More →
The landscape of higher education evolves every year, and, like you, Nexford University is keeping up with the trends. ...
Read More →
Nexford University's alumni see remarkable career growth with high promotion rates, salary increases, and leadership roles, proving the value of ...
Read More →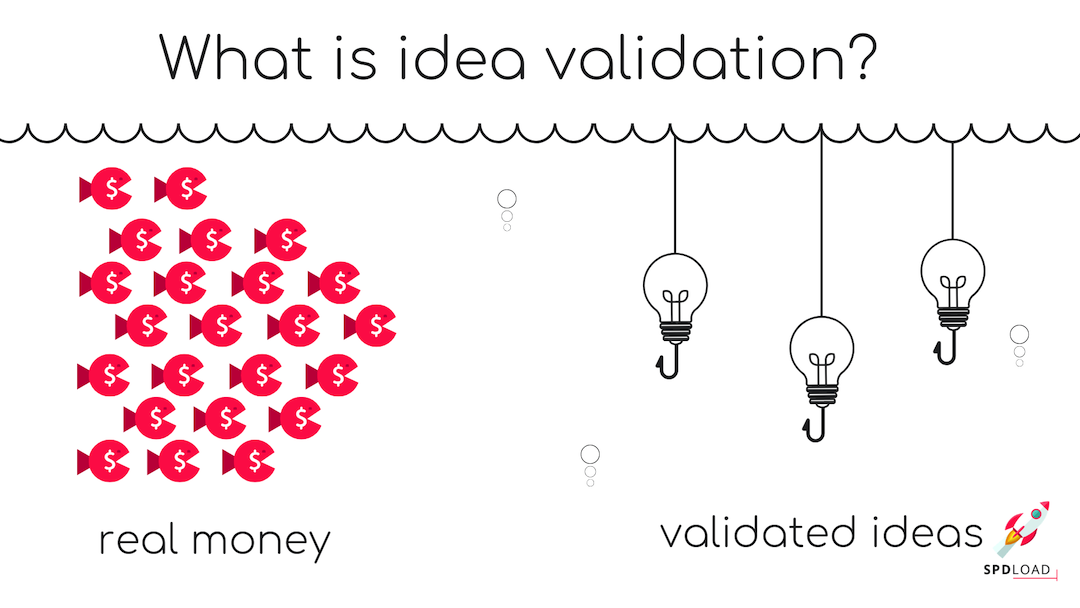
Every entrepreneur begins with an idea. That initial spark often carries an alluring sense that it's "the one"—the key to ...
Read More →
It’s a pretty normal day in Adis Ababa, Ethiopia, but not for Saron Habtemichael. It’s never business as usual for ...
Read More →
Do you aspire to run a company someday? Does the idea of spotting and acting on profitable opportunities excite you? ...
Read More →
Any business worth its salt needs to embrace digital transformation, but at the same time, hire and retain top talent ...
Read More →
Fuelled by the pandemic, the last two to three years has seen the tech industry explode with more career opportunities ...
Read More →
Choosing to be a post-graduate MBA student isn’t an easy decision to take. You already have a lot on your ...
Read More →
Evelyn Nyarega is a real dynamo. At the tender age of 53 she refuses to sit around and amble towards ...
Read More →
For some years now Africa has been touted as an emerging economic power and slowly but surely, that prediction is ...
Read More →
‘Jide Adeyemi is not one to stand still. Be that in business, life, and the country that he may find ...
Read More →
When you look up the term multitasking in the dictionary it says, ‘see Sarah Kamau’. Not only was she multitasking ...
Read More →
Mornay Schoeman has set out an action plan for her work and personal life and judging by her task-oriented demeanor ...
Read More →
Access to quality higher education in South Africa is constantly proving to be the difference between the supply of skills ...
Read More →
With more than half of Ghana’s workers experiencing an education mismatch with their roles, and traditional educational institutions struggling to ...
Read More →
Wisdom Ofori is a highly creative graphic designer and CEO of a well-known business called Design Plus Graphics, which he ...
Read More →
When the going gets tough, the tough get going. That is the kind of the mantra that Hesbon Oenga lives ...
Read More →
They’ve seen it all. Good CVs, bad CVs, and sometimes, fake CVs. But what headhunters are truly looking to see ...
Read More →
When you live in a city where everything happens at 100 miles per hour, it stands to reason that you’ll ...
Read More →
As a man for all seasons, Richard Yeboah has all that it takes to take on the most demanding jobs ...
Read More →
To succeed in today’s market, business leaders must learn to protect the brand, eke out a sustainable competitive advantage, and ...
Read More →
What could be better than spending every day of your waking life living near the shadow of Table Mountain in ...
Read More →
Alero Boyo currently works as Team Lead, Digital Partnerships at Tangerine Africa and took precious little time in making an ...
Read More →
Technology is progressing rapidly across the world and the African continent. This is opening the door to more opportunities for ...
Read More →
An MBA degree can be your ticket to much better career prospects. Not only will you be able to reach ...
Read More →
Failure to attract learning and development initiatives or not knowing what to measure against, often impacts business growth and employee ...
Read More →
We all know how long the application process for a degree can be. So, when should you apply for it ...
Read More →
Matthew Olugbemi works as a Product Owner on Nedbank’s Super App “Avo”, a mega e-commerce app that has over one ...
Read More →
Beatrice Ani is a resident of Nairobi, Kenya. Although not native to those parts, she is becoming the talk of ...
Read More →
Machine Learning is one of the fastest-growing industries in the world. It has seen a huge increase in interest and ...
Read More →
With the latest crop of Nigerian lecturer strikes having a devastating effect on students, many are asking exactly what their ...
Read More →
Ezekiel Akpan lives in Accra, Ghana. He is setting the tech world on fire with his in-depth knowledge in the ...
Read More →
In the past, when most people hung up their academic pursuits after graduating high school, college degrees and other forms ...
Read More →
All signs are pointing to a global recession. With a squeeze on economies and ripples felt in the job market, ...
Read More →
Virtual reality (VR) has potential to take learning beyond the traditional online learning experience, delivering enhanced engagement, improved retention, and experiential ...
Read More →
For decades, the job market had not changed much until COVID-19 came and revolutionized how people work, where they work, ...
Read More →
MBA graduate Anuoluwapo Ademuyiwa has never taken no for an answer, rather choosing to push the boundaries of business and ...
Read More →
What does your personal brand say about you? Is what you project what is perceived? To stand out from the ...
Read More →
If you’re planning on growing your career or successfully starting a business in the tech industry, there’s no better and ...
Read More →
The average person will go on many job interviews across their career, so it is imperative to stand out from ...
Read More →
The dawn of the new Information Revolution presents new opportunities for entrepreneurs. Global connectivity allows small companies and individuals a ...
Read More →
Digital age leaders have the power to inspire, engage and lead others, but must focus on building their communication skills ...
Read More →
Nexford is a next-generation online university based in Washington DC. Earn a globally affordable, accredited degree program at a flexible ...
Read More →
The traditional university experience has not changed for decades until online learning came along. Now it’s not just the location ...
Read More →
MBA graduate Azeez Olawale-Arish Yusuff wasted no time in putting his Nexford MBA specializations to work, delivering projects that moved ...
Read More →
As we start our fourth year, here are some of the initiatives we’re launching to help add more value to ...
Read More →
If you’re looking to get a leg up in business or change your career path, the 2022 list of the ...
Read More →
Looking at where you’ve come from and where you’re headed is normal for any birthday. Nexford’s third birthday celebration is ...
Read More →
Two-thirds of business school programs have seen applications increase during the pandemic, with MBAs leading the way. ...
Read More →
Iyinoluwa Aboyeji, co-founder of Flutterwave reckons it’s a blend of spotting a gap in the market and making an educated decision to go for it ...
Read More →
Electric Vehicles have the propensity to help lower carbon emissions, provided of course there is an uptake and skilled professionals ...
Read More →
Unemployment has long been an issue, especially since the 2008 financial crisis turned economies and labor markets on their heads ...
Read More →
Marketing has always been important in business as nobody will buy products or services if they don’t know about them ...
Read More →
Fad, buzzword, flash in the pan? Is online learning here to stay, or will people soon be returning to the ...
Read More →
With global warming and climate change worsening, society has developed more environmentally friendly ways of living and doing business ...
Read More →
Nigeria’s creative sector can potentially unlock the country’s economy and provide increased employment opportunities for the youth ...
Read More →
Recent MBA graduate Rebecca Ebokpo has wasted no time and already has her sights set on the future ...
Read More →
Recent MBA graduate Jason Weimer might live in Bangkok but he has his sights set on the global expansion of ...
Read More →
Alumni satisfaction is critical to the success of Nexford and learners. It’s why we commission regular surveys to gauge levels ...
Read More →
The face of the finance industry is dramatically different today. Is an MBA worth it to help advance your career? ...
Read More →
Is an online MBA worth it? Many are saying yes because a modern-day MBA leads to promotions, pay raises and better ROI ...
Read More →
Over the years, the uses for blockchain have grown significantly. What does it mean for businesses and startups ...
Read More →
Online learning became the center of attraction due to COVID-19. But it’s not the only reason why people are signing ...
Read More →
Only two decades ago, technical competencies were the most sought-after skills in the job market. Now, rapid innovation means employers ...
Read More →
Cryptocurrency is becoming so widely adopted that everyone from car manufacturers to universities are following suit ...
Read More →
It’s actually yourself. Read on to find out how to go about making that investment, and what your best option is ...
Read More →
The BPO industry is growing exponentially year on year, bolstering the economy, and at last count employed 1.3 million Filipinos ...
Read More →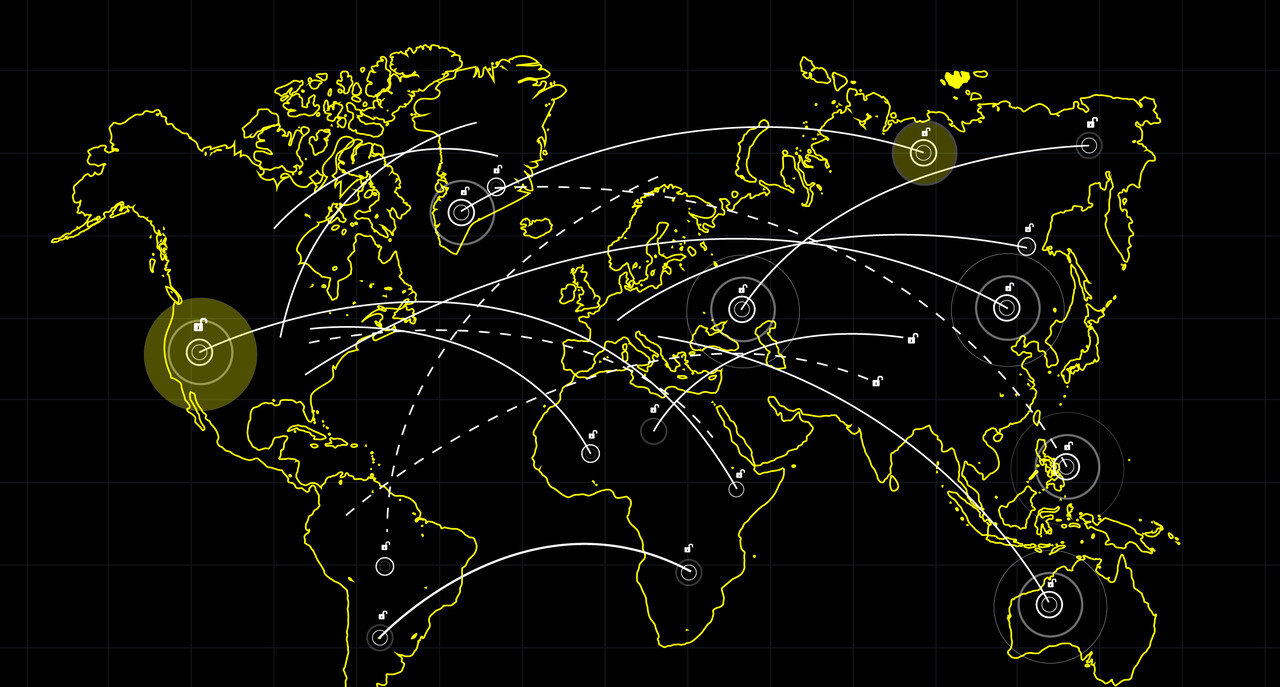
Developing countries represent an untapped wealth opportunity and may offer the most potential for the world’s economy ...
Read More →
The future of work is increasingly online. Read on to learn how the value of online degrees compares to traditional ...
Read More →
Many popular entrepreneurs are successful despite not pursuing higher education. However, there are many reasons why you should get a ...
Read More →
When the global pandemic happened, Kevin McFadgen knew his opportunity had arrived: earn the bachelor’s degree he has always dreamed ...
Read More →
Nexford was named the ‘Most Innovative Higher Education Brand, US’ at the Global Brands Awards 2020 ...
Read More →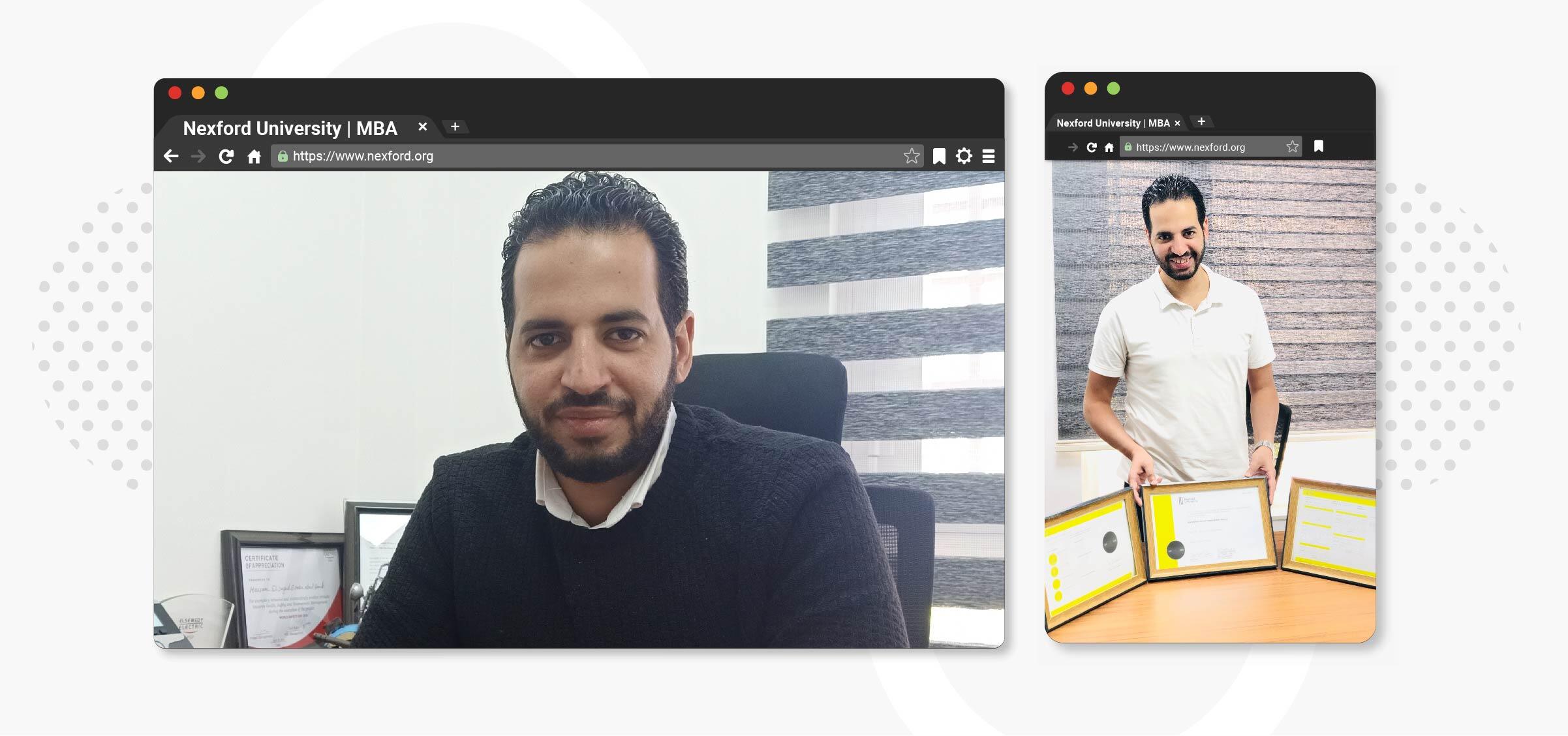
Ahmed Elmasry earned his MBA in just five months after getting stuck abroad in a global pandemic – and opting ...
Read More →
The 2019-20 survey results are in! 96 percent of learners would recommend Nexford ...
Read More →
Access to quality higher education in Kenya is constantly proving to be the difference between the supply of skills needed ...
Read More →
Nexford is less expensive than other universities and learners can graduate faster than the average ...
Read More →
Three industry heavyweights give their predictions for online learning in the aftermath of COVID-19 ...
Read More →
Amid the coronavirus pandemic, we celebrate our rising stars: meet our #NXUGrads ...
Read More →
Startup founder and former deputy head at one of the fastest-growing hotel chains in the world won’t stop now ...
Read More →
Nexford has been selected as an Extreme Tech Challenge finalist to solve the world’s most extreme problems ...
Read More →
Essential Futures Scholarship to empower 15 residents of the Washington DC metro area ...
Read More →
Maximize your success from day one and learn how to submit the perfect Nexford application ...
Read More →
COVID-19 restrictions might have temporarily put CEO and Chief Brand Strategist ‘Jide Adeyemi’s travel plans on pause, but his long ...
Read More →
The global pandemic has put online connections at the heart of how we work – online learning is more important ...
Read More →
Developing nations should lead the charge towards bridging the digital divide, says MTN’s Chairman of the Board Ernest Ndukwe ...
Read More →
With 20+ years of banking experience, Sterling Bank’s CEO, Abubakar Suleiman, shares tips for a successful career ...
Read More →
A brand-new alliance between business networking platform LinkedIn and the online university opens up a world of opportunity for Nexford ...
Read More →
Get up-to-speed with one of the latest remote-working global trends and download Nexford’s desktop virtual backgrounds for Zoom ...
Read More →
Graphic designer Jason Weimer’s passion for business and entrepreneurship has led him to the other side of the world ...
Read More →
The fourth industrial revolution is disrupting almost every industry around the world, while teenagers leave school with the same skills ...
Read More →
We still live in a world where your place of birth can dictate your chances of success. At Nexford, we’re ...
Read More →
When you want to be a neurosurgeon and an entrepreneur, there’s no obvious path to take when you leave high ...
Read More →
We’re not like any other American university. Our learners come from all corners of the globe. That’s the way we ...
Read More →
As the door to 2019 closes, we look into what possibilities the opening of 2020 might bring. Here are some ...
Read More →
2020 is just around the corner and we want to ensure you enter the New Year the right way. Here ...
Read More →
As humans, we hold the power. The power to reach our full potential and reach new limits together. Question is, ...
Read More →
When it comes to technology, agile thinking is your best bet. Thought leader Jill Rosenberg shares her top tips for ...
Read More →
Founder & CEO of Nexford, Fadl Al Tarzi, shares his knowledge of operating from the ideation to IPO with purpose ...
Read More →
Most of the 660 million people on LinkedIn aren’t getting the best out of the world’s most powerful professional social ...
Read More →
Gone is the idea that learners attend a bricks and mortar university fresh out of school. Today’s learners are diverse, ...
Read More →
The worldwide demand for higher education is outstripping supply. Dr Jay Halfond shares his insights into addressing a critical global ...
Read More →
Discover your unique strengths and learn to set meaningful career development goals ...
Read More →
Bitesize learning. Anytime. Anywhere. Efficient, effective and flexible. It’s the study style of the future ...
Read More →
Flexible, affordable, recognized – and what employers want. Find out why online learning could be for you ...
Read More →
Need financial support for your studies? Here’s what you need to know ...
Read More →
Why our learners master valuable real-life skills for the global workplace from day one ...
Read More →
Our flexible approach to learning means you can fit in your studies around your life. But you’ll need to be ...
Read More →